Renzulli Creativity Programs are based upon decades of research and practical experience in thousands of classrooms across the globe [www.gifted.uconn.edu]. The programs combine several educational principles that allow participants to achieve levels of learning and creative thought not available in traditional classrooms. Various organizational and delivery options (discussed below) allow for different arrangements based on local program requirements and circumstances.
The programs incorporate four research-based subtheories: the Three-Ring Conception of Giftedness, the Theory of Blended Knowledge, the Enrichment Triad Model, and Executive Functions. Renzulli Creativity Programs also utilize technology that allows students to access the wider world of knowledge by learning how to use Just-In-Time (J-I-T) knowledge acquisition techniques.
Subtheory I: The Three-Ring Conception of Giftedness
The Three-Ring Conception of Giftedness attempts to portray the main dimensions of human potential for creative productivity. The name derives from the conceptual framework of the theory—namely, three interacting clusters of traits (Above Average Ability, Task Commitment, and Creativity) and their relationship with general and specific areas of human performance.
Perhaps the most salient aspect of this theory is that it is the interaction among these clusters of traits brought to bear on a particular problem situation that creates the conditions for the creative productive process to commence. A second aspect of the theory posits that whereas abilities (especially general intelligence, specific aptitudes, and academic achievement) tend to remain relatively constant over time, creativity and task commitment are contextual, situational, and temporal.
Finally, these clusters of traits emerge in certain people, at certain times, and under certain circumstances. The Enrichment Triad Model (discussed below) is the compatible learning theory from which educational conditions are provided that create the conditions for stimulating interaction between and among the levels of knowledge described below.
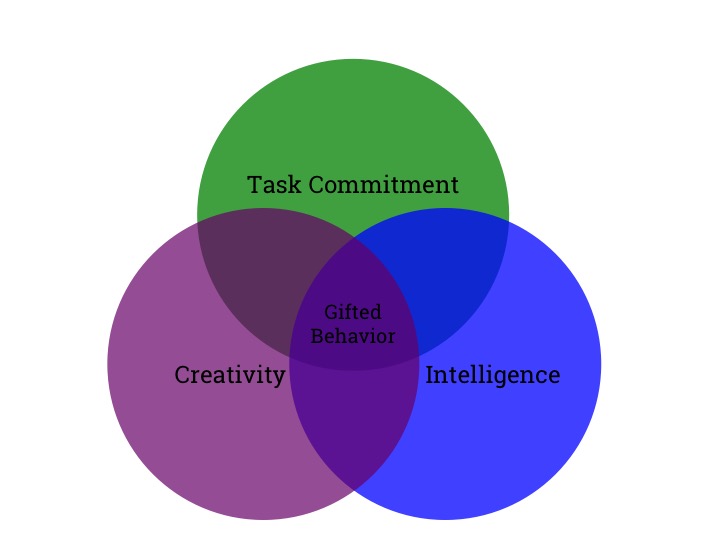
The Three-Ring Conception of Giftedness
Subtheory II: Blended Knowledge
Blended Knowledge combines the three levels of knowledge required to achieve the goal of Creative Productivity:
- Received Knowledge includes traditional instruction of facts, vocabulary, numeracy and other data derived from textbooks and lectures. This information is usually assessed through standardized testing and provides the foundation for more advanced levels of knowledge.
- Analyzed Knowledge develops thinking skills, which include interpreting, extrapolating, comparing and contrasting, ranking, prioritizing, determining cause and effect, and making analogies. These higher level skills are achieved through discussion, debates, critiquing and questioning which foster the development of advanced analytical skills.
- Applied and Created Knowledge is the most advanced level of problem solving and construction of knowledge, but it requires curiosity, creativity and task commitment to achieve this level of competence. Individuals that possess these abilities are highly productive and creative, which enables them to become successful contributors in their respective fields through the development of original ideas, materials and products.
The benefits of Blended Knowledge mastery are listed above and are part of our mission of guiding students toward thinking, feeling, and carrying out creative and investigative work like practicing professionals, even if they are working at more junior levels that adult scientists, writers, designers, filmmakers, or entrepreneurs.
Subtheory III: Enrichment Triad Model
The instructional methods used at Renzulli Creativity Programs include the Enrichment Triad Model, which allows students to solve problems through:
Type 1 Enrichment – General Exploratory Experiences
Exposure to ideas, topics, and areas of potential interest not ordinarily covered in the regular curriculum. The purpose of Type I enrichment is to give students a wide variety of options from which they might want to pursue advanced study.
Type 2 Enrichment – Group Training Activities
Provides systematic training in the following six areas:
- Cognitive Thinking Skills
- Character Development and Affective Process Skills
- Learning-How-To-Learn Skills
- Using Advanced Research Skills and Reference Materials
- Written, Oral, and Visual Communication Skills
- Meta-Cognitive Technology Skills
Type 3 Enrichment – Individual and Small Group Investigations of Real Problems
Application of the above skills to a self-selected problem or area of interest that results in a product designed to have an impact on an intended audience.
The combination of these enrichment activities fosters Creative Productivity through learning in a natural environment rather than a highly structured environment. The use of these three interrelated types of enrichment is modeled after the modus operandi of practicing professionals in the adult world.
Subtheory IV: Executive Functions – Leadership for a Changing World
The fourth and final theory enables individuals to pursue a desired goal in an efficient and effective way. The most creative ideas, advanced analytic skills, and the noblest of motives may not result in positive action unless leadership skills such as organization, sequencing, and sound judgment, self-regulation, and time management skills are brought to bear on problem situations.
Executive functions are broadly defined as the ability to engage in novel situations that require planning, decision making, troubleshooting, and compassionate and ethical leadership that is not dependent on routine or well-rehearsed responses to challenging combinations of conditions.
It has been argued that great leadership works through non-cognitive traits such as self-awareness, self-management, motivation, empathy, and social skills. There is general agreement among researchers that the so-called “Big Five” personality traits are the basis on which talent development programs should focus:
- Openness—Inventive and curious as opposed to consistent and cautious
- Conscientiousness—Efficient and organized as opposed to easy-going and careless
- Extraversion—Outgoing and energetic as opposed to solitary and reserved
- Agreeableness—Friendly and compassionate as opposed to cold and unkind
- Positive Self-Concept—Secure and confident as opposed to sensitive and nervous
These skills have important implications for the academic success of students, career decisions, and even the economic productivity of nations. Although not minimizing the importance of traditional cognitive ability, these authors point out that conventional assessments account for a small portion of the variance when examining long-term academic and career accomplishment, especially as it relates to the advancement of adult competencies in highly demanding professions where leadership skills and creative productivity are the criteria for success.
These functions are especially important to highly capable people because of the positions of leadership and influence to which they typically ascend.
Assessment Data
We have collected substantial Assessment Data, which demonstrate the Schoolwide Enrichment Model produces positive results in the subject area of the project, reading comprehension, as well as student motivation.
Additional Assessment Data and references are available upon request.
References and Research
- References and Links to Research are available at: www.gifted.uconn.edu
- Schoolwide Enrichment Model (SEM) Resources are available at: http://www.gifted.uconn.edu/sem/
- Sample Projects are available at: http://www.gifted.uconn.edu/sem/typeiisp.html
- Additional Assessment Data is available upon request
Organizational and Delivery Options
Renzulli Creativity Programs can be delivered to students in highly concentrated, infusion based, or project based options.
1) Concentrated Delivery Options
Concentrated delivery programs allow students to select and focus upon their academic passion in an environment where more time and focus can be applied to a problem or area of study. These options include:
- Summer Programs (Residential and Day)
- After School Programs
- Small Group Research and Investigative Projects (See Enrichment Clusters described below)
- Weekend Programs
2) Infusion of Enrichment Activities into Advanced Curriculum
Research projects can be offered as stand-alone enrichment opportunities or infused into a standard curriculum, AP or IB curriculum, or advanced honors courses.
Curriculum infusion incorporates these projects into the lesson plan, whereby teachers help students to go beyond the standard curriculum to achieve the highest levels of learning and creativity.
3) Whole School Approaches — The Schoolwide Enrichment Model Approaches
Schools can utilize the Schoolwide Enrichment Model described above as uses the infusion based approach to make prescribed curricular content more interesting and engaging. This approach allows schools to enhance their curriculum through:
Development of a Total Talent Portfolio For Each Student
The total Talent Portfolio documents each student’s academic strength areas, interests, learning styles, and preferred modes of expression. It is used in all aspects of developing personalized learning plans including curricular modifications, options for enrichment cluster selection, and guidance for selecting and pursuing Type III enrichment projects.
Enrichment Clusters
All learning exists on a continuum that ranges from deductive and prescriptive learning on one end to inductive, self-selected and investigative learning on the other end.
Medium sized school might offer 15-20 enrichment clusters. The number of students in each cluster will vary based upon student interest and teacher requirements for effective participation. Teachers develop individual and small group learning situations based on their own strengths and interests, sometimes working in teams that include parents, mentors, and community members. To understand the problem and to develop a solution, students must investigate, research and use creativity and communicate with their team to formulate their proposal. This Authentic Learning is the vehicle through which students develop basic and advanced cognitive skills. Students’ research enables them to use technology to find Just-In-Time (JIT) information that is relevant to their projects, which is the same process employed by professional researchers for the creative and investigative process.
Curriculum Compacting For High Achieving Students
Curriculum Compacting is a systematic three-step process for eliminating curricular material that students have already mastered and replacing it with more challenging and highly engaging learning activities.
The Schoolwide Enrichment Model (SEM) uses the infusion based approach to make prescribed curricular content more interesting and engaging and helps to stimulate the three Es: Enjoyment, Engagement and Enthusiasm for learning.
